Introduction for the Process of Resin Transfer Molding (RTM)
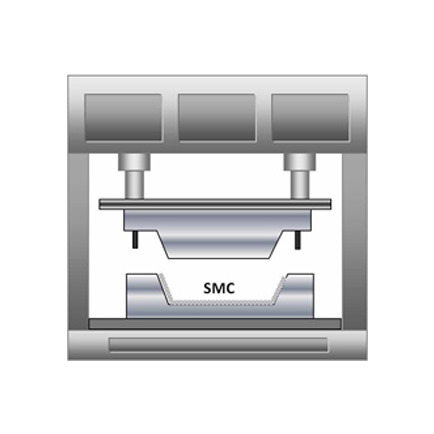
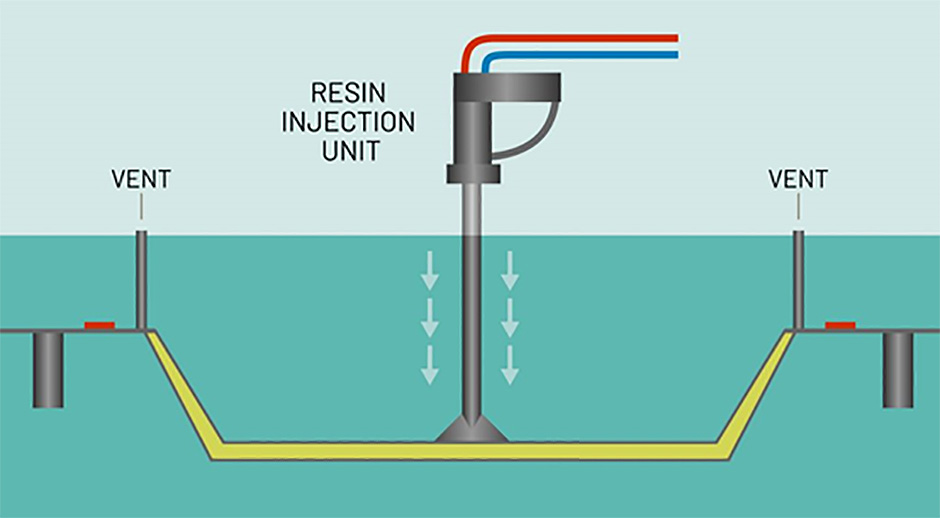
How Resin Transfer Molding Works?
The process typically involves the following steps:
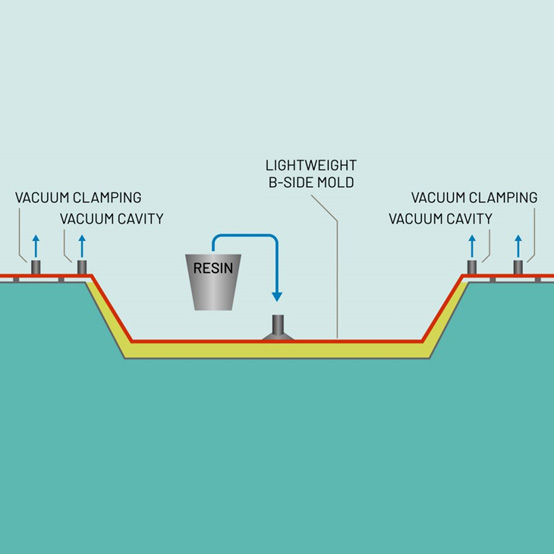
● A dry fiber preform, such as fiberglass or carbon fiber, is placed in a closed mold.
● The mold is clamped shut, creating a sealed cavity.
● Resin is injected into the mold at low pressure, displacing the air and impregnating the fibers.
● The resin cures under controlled temperature and pressure conditions.
● The finished part is removed from the mold.
RTM offers several advantages, including the ability to produce complex shapes with high fiber volume fractions, excellent fiber wet-out, and reduced void content. It also allows for better control over resin flow and minimizes the risk of resin-rich or dry areas in the final part. However, RTM requires specialized equipment and tooling, and the process can be more time-consuming compared to other molding techniques.
RTM can be used in a variety of fields. In automotive industry, it is employed to manufacture lightweight, high-performance parts, such as body panels, engine components and suspension systems. These components can help reduce vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency. In medical devices, RTM is used to manufacture production of medical devices and implants, such as orthopedic implants, catheters and surgical instruments. These components often require a smooth surface finish and excellent biocompatibility. In industrial equipment, RTM is used to manufacture components for industrial equipment, such as machine housings, conveyor systems, and robotic arms. These components can help improve equipment performance and reduce maintenance requirements.
✧ Product Drawing