Vacuum Infusion (VI)
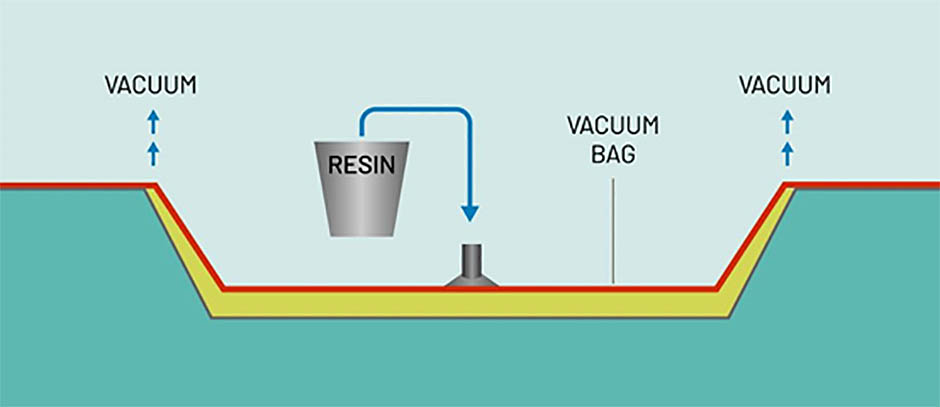
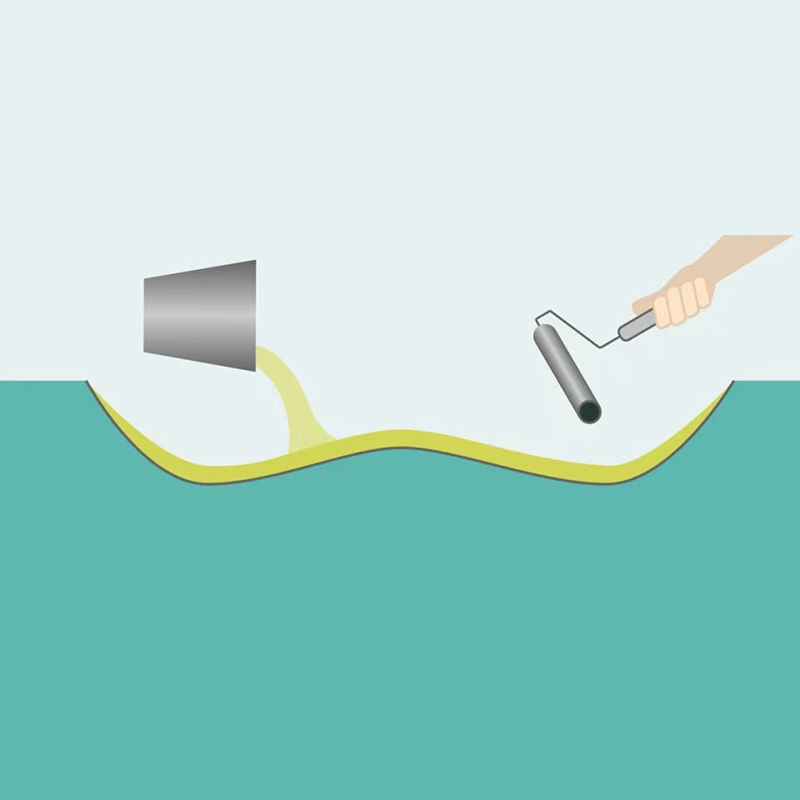
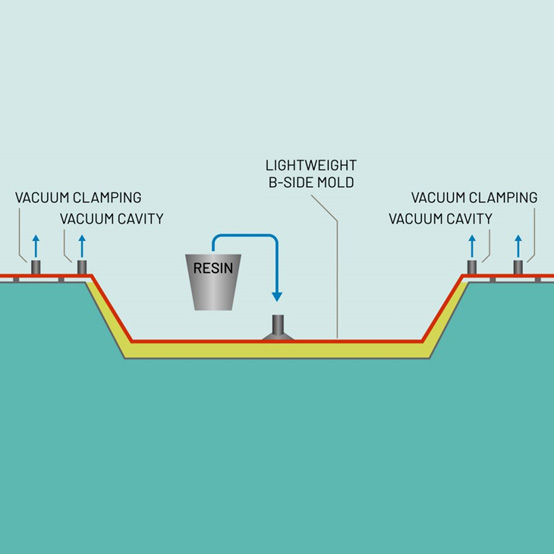
How Vacuum Infusion Works?
VI offers several advantages, including the ability to produce large and complex parts with high fiber volume fractions, improved fiber wet-out, and reduced emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) compared to traditional open molding techniques. However, it can be a relatively slow process and requires specialized equipment and tooling.
Some of the key advantages include:
● Preplacement of reinforcement can be employed to achieve optimum strength-weight ratios.
● Best choice for products with high strength-to-weight requirements, or with slight design returns, edge overhangs, or high draft angles that would cause dielocks on rigid B-side mould surfaces.
● Complex multilayer laminates with cores and inserts can be completed in a single step rather than as individual layers.
● Inmould gel coat finishes can be employed for desired cosmetic finishes.
Vacuum infusion has various applications across different industries and fields. For example, in automotive industry, vacuum infusion is used to manufacture lightweight components, such as engine blocks, suspension components, and body panels. This helps to reduce the overall weight of the vehicle, which in turn improves fuel efficiency and reduces emissions. In building and construction, vacuum infusion can be used to create insulating panels. In medical and healthcare, vacuum infusion is used for manufacturing various devices and components, such as catheters, stents, and medical sensors. This process helps to create strong, lightweight, and biocompatible devices that can be safely implanted in the body.
✧ Product Drawing